January 10, 2019
If only we could keep our bodies young, healthy and energetic, even as we attain the wisdom of our years. But now new research at the Weizmann Institute of Science suggests this dream could be at least partly obtainable in the future when it discovered that by aiding the immune system to clear away old cells in aging mice it helped restore youthful characteristics.
The research, led by Professor Valery Krizhanovsky and Dr Yossi Ovadya in the Molecular Cell Biology Department, was recently published in Nature Communications.
The research began with an investigation into the way the immune system is involved in a crucial activity: clearing away old, senescent cells that spell trouble for the body when they hang around. Senescent cells – not completely dead but suffering loss of function or irreparable damage – have been implicated in diseases of aging by promoting inflammation.
The researchers used mice in which a crucial gene for this immune activity was missing. At two years (elderly, for mice), the bodies of these mice had a greater accumulation of senescent cells compared with the mice in which the gene for removing these cells was intact. The mice missing the gene suffered from chronic inflammation, and various functions in their bodies appeared to be diminished. They also looked older – and died earlier – than their normal counterparts.
Next, the researchers gave the mice a drug that inhibits the function of certain proteins that help the aging cells survive in their senescent state, to see if this would contribute to the removal of these cells from the body.
The drugs were administered to mice whose aging was a result of the malfunctions the group had uncovered in the immune system as well as those suffering premature aging from a different genetic error.
The treated mice responded exceptionally well to the drug: Their blood tests and activity tests showed improvement, and their tissues appeared to be much closer to those of young mice.
The scientists counted senescent cells, finding many fewer of them remaining in the treated mice’s bodies; and when they looked for signs of inflammation, they found that this, too, was significantly lower. The mice treated with the drug were more active and their median lifespan rose.
The scientists intend to continue exploring ways to prompt the human body to remove its old senescent cells, particularly to find means of activating the immune system to do this job. That is, if future experimentation proves their theories correct, they could end up creating truly ‘anti-aging therapies.
The story in English has appeared in many publications: Medical Express, Science Daily, Life Extension, Neuroscience News, JWire, Innovation Toronto, Lab Roots, 24Mins_Fr, aazor.com, uneath.com, The Guardian (Nigeria), bionity.com plus more – see Google top hits.
Professor Valery Krizhanovsky’s research is supported by the Ilse Katz Institute for Material Sciences and Magnetic Resonance Research; the Rising Tide Foundation; the Quinquin Foundation, Mr and Mrs Bruce Kanter; and the European Research Council.

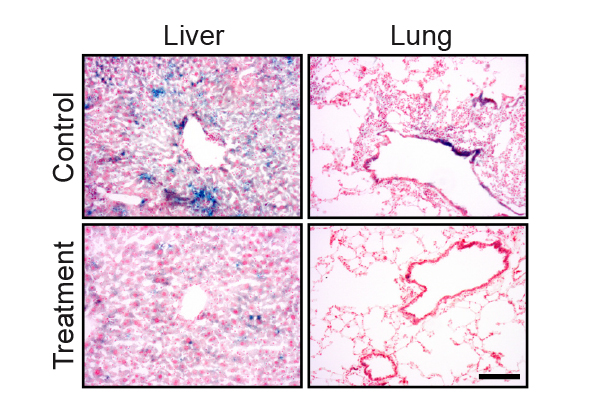
Drug treatment eliminates senescent cells from tissues of old mice. The blue staining shows senescent cells in lung and liver tissue. The amount of the staining is significantly reduced following the drug treatment