Although over the centuries we have learned much about our physical world, from the earth below to the stars above, there are still many mysteries to uncover.
With curiosity and a thirst for knowledge as the drivers of Weizmann Institute scientists, they are working hard to unlock the doors to these answers. Weizmann archaeologists were the first to find a way to precisely identify and analyse prehistoric ashes and discovered a pure, well-preserved DNA source in fossilised bone. Weizmann material scientists and structural biologists also revealed that shell and bone form in a similar way and its astrophysicists for the first time watched a massive star – estimated to be a mass of 200 suns – turn supernova to black hole. Weizmann hydrologists work towards aiding the development of sound environmental policies by providing models of how groundwater moves. Overall Weizmann is looking at the past to understand the future of our planet and universe works.
Weizmann facts
First to watch a star turn supernova then black hole
Helped prove in 1957 that ‘gluons’ – responsible for natures strongest force – exist
Showed that 50% of the mineral dust feeding the Amazon is from one small African valley
Calculated that when holding up one grain of sand to the sky, the part it covers contains 10,000 galaxies
Selected Achievements
Seeking to unlock the doors to secrets hidden in our lost worlds
Fossilised DNA was found that it could be preserved and less prone to contamination with modern DNA, allowing DNA fragments held in crystal aggregates within fossilised bone to be isolated and studied. This Weizmann science by Professor Steve Weiner and colleagues is increasing insight into our past as well as our future.
Seeking understanding of why Amazon rainforests are so abundant
Over half the mineral dust carried through the air to settle in the Amazon basin was discovered by Weizmann’s Professor Ilan Koren to come from one small valley in the African Sahara. When measured using satellite images, this dust provides the wonderful Amazon rain forest with its nutrients.
Seeking the strongest force in nature
Gluons are the force that holds the nucleus of an atom together and Weizmann scientists were part of research in 1957 that proved they existed. As atoms are part of all beings and structures, gluons are therefore the strongest force in nature.
Latest News
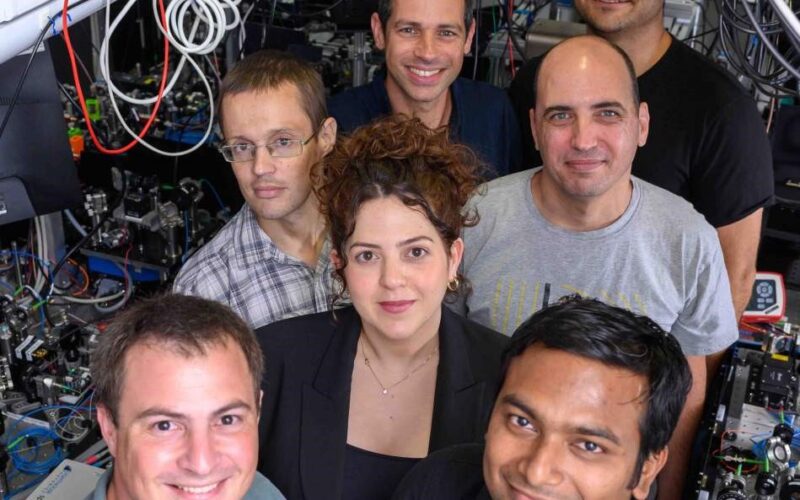

When the Light Particle Saw the Light
A Weizmann Institute study of photons in quantum computing has made a surprising discovery: When photons collide, they create vortices. Vortices are a common physical phenomenon. You find them in…
Beating the Plateau
Weizmann Institute of Science researchers have established absolute chronology for Kingdom of Judah’s Jerusalem. Jerusalem has been inhabited continuously for thousands of years, serving as both a center of religious…
A Hundred Million Suns: The Most Complete Portrait of a Supernova
Humankind has long turned to the skies in search of answers. Accounts of supernovae – exploding stars – go back thousands of years, but while we know today that these…
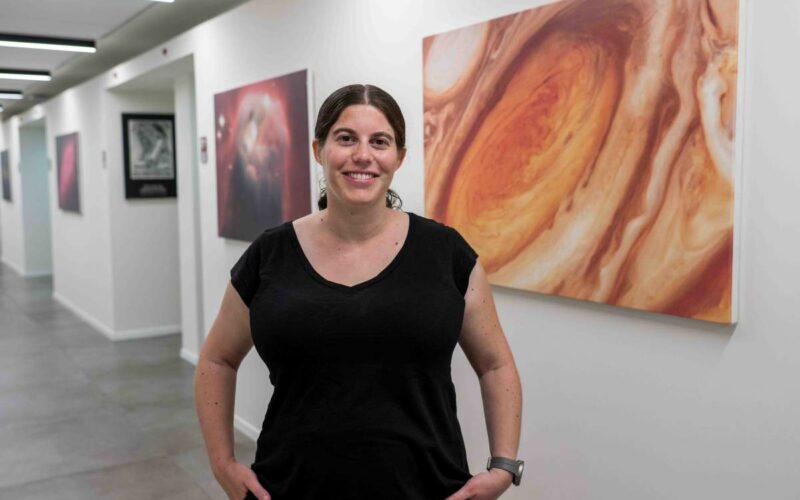

A ‘Jupiter’ Hotter than the Sun
A newly discovered binary celestial system via special data analysis led by the Weizmann Institute of Science, may advance our understanding of planet and star evolution under extreme conditions. The…
Other achievements
Advancing Technology
Weizmann’s research into advanced technology is immense and acts as a time line for technology’s evolution.
Fighting Cancer
Nearly half the life science research at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel is focussed on cancer.
Improving Health and Medicine
Pioneers in research that has lead to better health and medicine world-wide, Weizmann has a long list of achievements.
Protecting our Planet
Providing solutions to our planet’s environmental challenges is part of Weizmann’s business.
Enriching Education
Science education is a core endeavour of the Weizmann Institute of Science.
