March 6, 2023
Sometimes anticancer antibodies press on the gas and the brakes at the same time. New research from the Weizmann Institute of Research in Israel might help them accelerate better.
When driving, putting a foot on the gas or brake pedal controls the car’s speed. This also happens in our body when driving an immune response. Like human drivers, antibodies have a ‘foot’ – a sort of molecular limb that ‘presses’ the gas and brake pedals. Those pedals are receptors on the outer membranes of immune cells: When an antibody foot binds to one of these pedals, it can either speed up the immune response or slow it down.
Among their other uses, antibodies are employed in a new generation of cancer treatments known as immunotherapy, which harness the immune system’s natural capabilities to fight malignant tumours. Importantly, as far as these cancer-fighting antibodies are concerned, speed is of the essence.
The new Weizmann study, conducted by a team of researchers headed by Dr Rony Dahan, revealed that a small molecular change in a common immunotherapy antibody might enable it to bind better to certain ‘gas pedal’ receptors, thus accelerating the immune response against cancer.
The study just published in Science Immunology, also shows that adding a second antibody – one that blocks inhibitory receptors – may improve the effectiveness of anticancer treatments.
In 2016, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved a breakthrough immunotherapy treatment that uses antibodies to block a protein called PD-L1. Cancer cells can exploit PD-L1 to suppress the immune response against them by ‘exhausting’ the T cells that fight the cancer. The antibodies in current use were designed to operate in a direct manner: They neutralise PD-L1, thus preventing it from binding to T cells and exhausting them.
In a previous study, Dahan discovered that antibodies to PD-L1 could also act in an indirect manner, not only neutralising the protein but also binding to receptors on immune cells and activating them against the cancer cells expressing PD-L1. That study, which suggested that the antibodies enhanced the treatment’s effectiveness, was carried out with mouse antibodies, rather than the human version used in cancer treatments.
In the new study, Dahan and his team in Weizmann’s Systems Immunology Department checked whether the findings are valid for the drugs meant for humans.
To this end, the scientists used so-called humanised mice, in which genetic engineering was used to replace mouse antibody receptor genes with human ones. After inducing tumours in these mice, the scientists treated them with two clinically used antibodies: one that cannot bind immune cell receptors (the drug atezolizumab) and one that can (the drug avelumab).
Led by research student Noy Cohen Saban, the team followed the growth rate of tumours in the two groups of mice. Since the scientists knew that the binding antibodies also activated cancer-fighting immune cells, they were surprised to discover that there was no significant difference between the groups. Why did the human version of the drug not perform as it had in regular mice?
The researchers knew from past studies that, while the binding of antibodies to most receptors acts as a gas pedal that enhances the immune response, there is one receptor that acts as a brake pedal, and binding to this one inhibits the response. A closer look revealed that, compared with similar cells of other organs, there were many more of these brake pedal receptors on certain immune cells in the tumours’ microenvironment. That phenomenon was observed in human tumours as well. In tumour samples of skin and kidney cancers, which were obtained through the University of Michigan, the scientists identified an increased expression of the immune-suppressing receptors.
In other words, despite the drug’s boost to the immune system, the total effect was something like pressing the gas and brake pedals at the same time. Once the scientists realised what was happening, they tried the experiment again, this time giving the mice a combined treatment of avelumab and a second antibody that had been proven to inhibit the immune-suppressing receptors. With the foot lifted from the immune system’s brakes, the cancer treatment was much more effective.
The researchers thought they might be able to make the antibodies even more effective by getting them to press harder on the ‘gas pedals’ – that is, they looked for a way to make the antibodies’ ‘feet’ bind more tightly to the immune-enhancing receptors. They created a small change in a sugar molecule associated with the antibody’s foot – a change that can increase the binding affinity of an antibody eleven-fold.
Following treatment with the new, improved antibodies, the size of the tumours in humanised mice was smaller, and the treated mice’s average survival time was longer.
Finally, the team delved into the mechanism of action responsible for the success of their improved antibody. They found that this antibody gave the anticancer treatment a double advantage: It was able to both increase the numbers of T cells penetrating the tumour and to decrease the numbers of certain myeloid cells – immune cells that inhibit the anticancer response in the tumours’ microenvironment.
“The findings of this research could undergo a rapid transition from the laboratory to the clinic, to improve those drugs already available to cancer patients,” said Dahan.
“Furthermore, the discovery of improved antibodies that act on immune cells other than T cells creates an opportunity to use them in treatments for certain still incurable cancers in which T cell-targeted therapies are ineffective.”
To date, the FDA has approved 96 immunotherapies based on seven antibodies to PD-L1/PD-1 for treating 24 distinct cancer indications.
The following researchers also participated in the study: Dr. Adam Yalin, Dr. Tomer Landsberger, Dr. Ran Salomon, Dr. Tali Feferman and Prof. Ido Amit of Weizmann’s Systems Immunology Department; and Prof. Ajjai Alva of the University of Michigan.

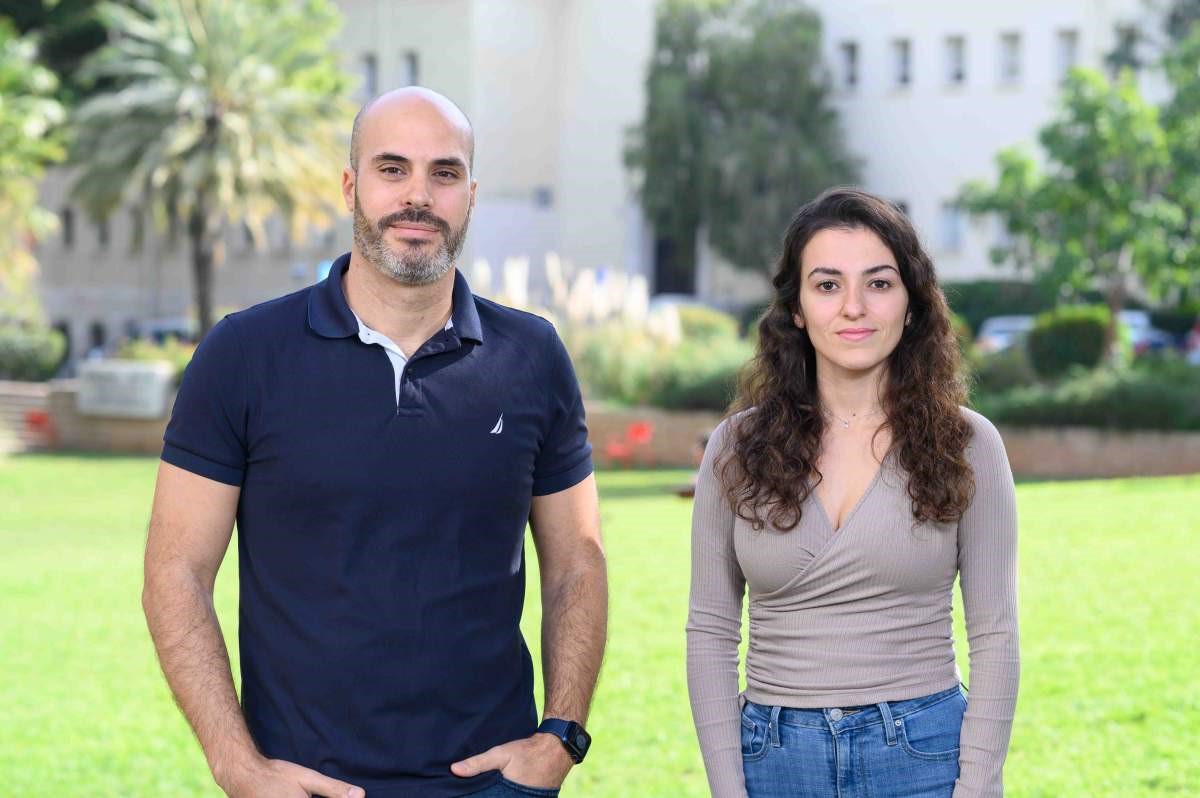
Dr Rony Dahan and Noy Cohen Saban. High octane immunotherapy
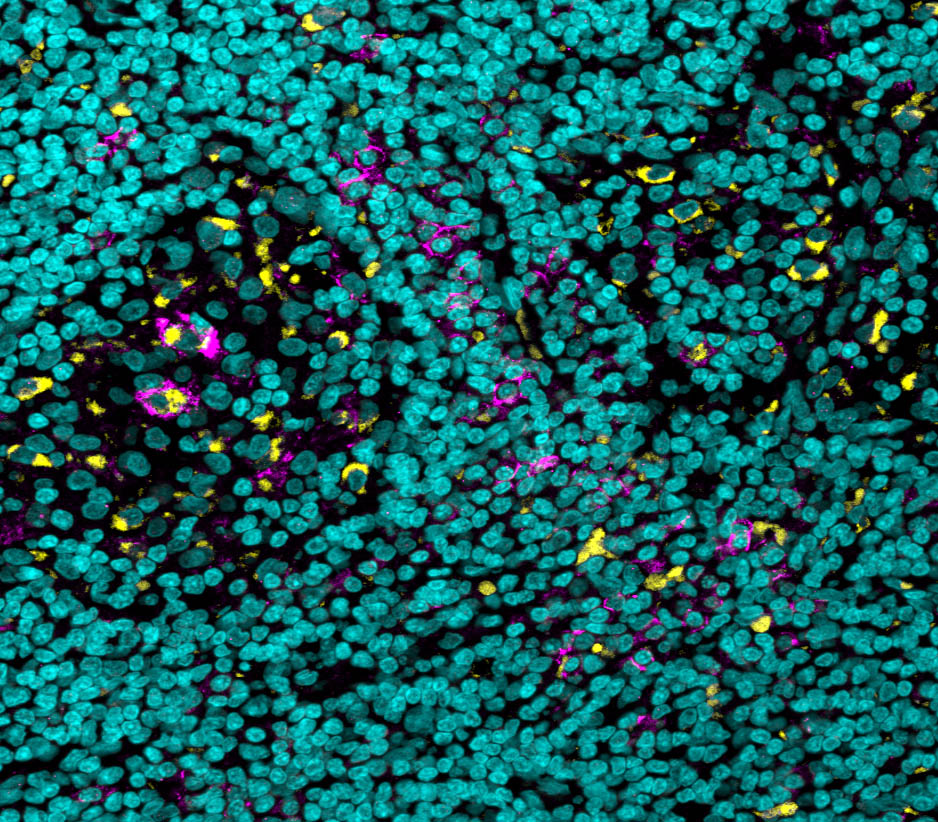
Tissue sample of a particularly aggressive skin cancer reveals immune cells (yellow) that express on their surfaces a “brake pedal” receptor called FcgIIb (purple); cell nuclei are in blue

Science Immunology featured Dr Rony Dahan's research on the cover of the journal’s March 2023 issue





