What did the very first proteins that appeared on Earth around 3.7 billion years ago look like? Now an experiment in recreating primordial proteins solves a long-standing riddle.
Professor Dan Tawfik of the Weizmann Institute of Science, and Professor Norman Metanis of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, have reconstructed protein sequences that may well resemble those ancestors of modern proteins, and their research suggests a way that these primitive proteins could have progressed to forming living cells.
Their findings were recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The proteins encoded in a cell’s genetic material are the screws, springs and cogs of a living cell — all of its moving parts. But the first proteins, we assume, appeared well before cells and thus life as we know it.
Modern proteins are made of 20 different amino acids, all of them essential to protein-building, and all arranged in the form of a polymer – a long, chain-like molecule – in which the placement of each amino acid is crucial to the protein’s function. But there is a paradox in thinking about how the earliest proteins arose. Because the amino acids needed to make proteins are themselves produced by other proteins – enzymes. It’s a chicken-and-egg kind of question, and it has only been partially answered until now.
Scientists believe that the very first true proteins materialised from shorter protein segments called peptides. The peptides would have been sticky assemblies of the amino acids that were spontaneously created in the primeval chemical soup; the short peptides would have then bound to one another, over time producing a protein capable of some sort of action. The spontaneous generation of amino acids was already demonstrated in 1952, in the famous experiment by Miller and Urey, in which they replicated the conditions thought to exist on Earth prior to life and added energy like that which could come from lightning or volcanoes.
Showing that under the right conditions amino acids could form without help from enzymes or any other mechanism in a living organism, suggested that amino acids were the ‘egg’ that preceded the enzyme ‘chicken’.
Tawfik, from the Institute’s Biomolecular Sciences Department, said: “This is all well and good but one vital type of amino acid has been missing from that experiment and every experiment that followed in its wake: amino acids like arginine and lysine that carry a positive electric charge.”
These amino acids are particularly important to modern proteins, as they interact with DNA and RNA, both of which carry net negative charges. RNA is today presumed to be the original molecule that could both carry information and make copies of itself, so contact with positively-charged amino acids would theoretically be necessary for further steps in the development of living cells to occur.
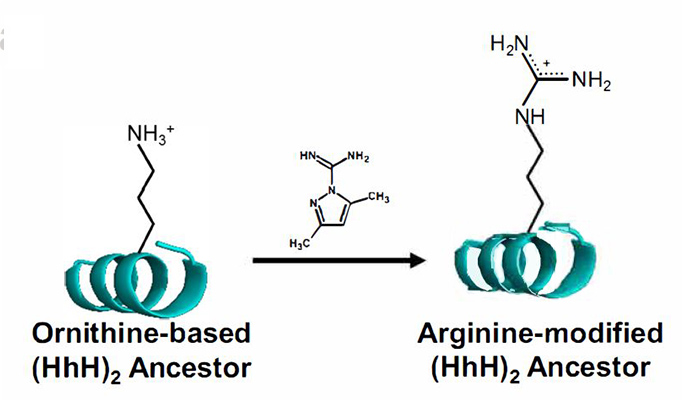
But there was one positively-charged amino acid that appeared in the Miller-Urey experiments, an amino acid called ornithine that is today found as an intermediate step in arginine production, but is not, itself, used to build proteins. The research team asked: What if ornithine was the missing amino acid in those ancestral proteins? They designed an original experiment to test this hypothesis.
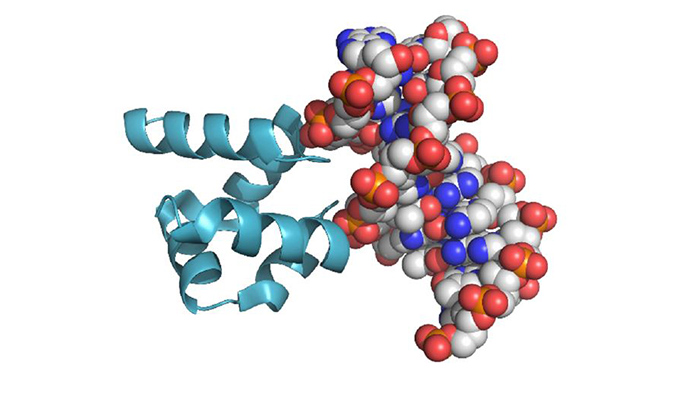
The scientists began with a relatively simple protein from a family that binds to DNA and RNA, applying phylogenetic methods to infer the sequence of the ancestral protein. This protein would have been rich in positive charges – 14 of the 64 amino acids being either arginine or lysine. Next, they created synthetic proteins in which ornithine replaced these as the positive charge carrier.
The ornithine-based proteins bound to DNA, but weakly. In Metanis’ lab, however, the researchers found that simple chemical reactions could convert ornithine to arginine. And these chemical reactions occurred under those conditions assumed to have prevailed on Earth at the time the first proteins would have appeared. As more and more of the ornithine was converted to arginine, the proteins came more and more to resemble modern proteins, and to bind to DNA in a way that was stronger and more selective.
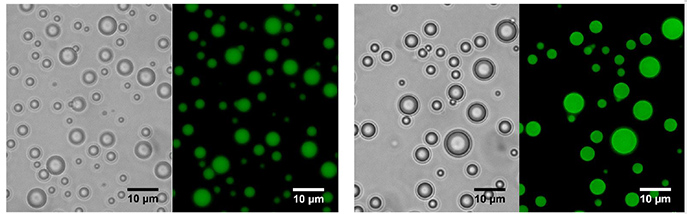
The scientists also discovered that in the presence of RNA, that the ancient form of the peptide engaged in phase separation (like oil drops in water) – a step that can then lead to self-assembly and ‘departmentalisation’.
“This suggests that such proteins, together with RNA, could form proto-cells, from which true living cells might have evolved,” concluded Tawfik.